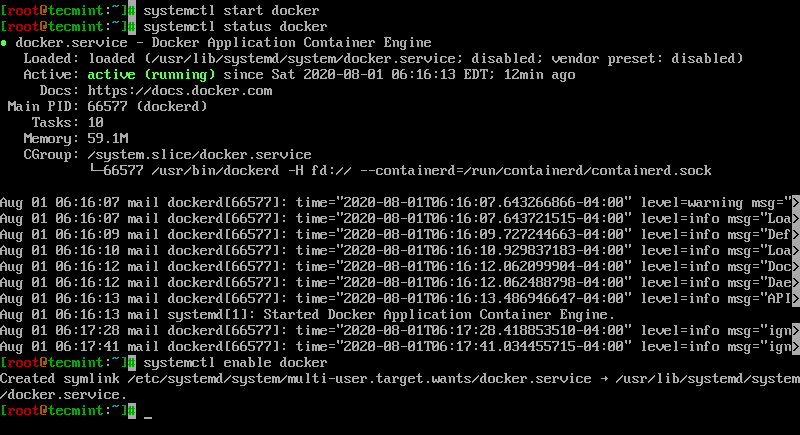
- /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service Permission Denied
- Docker /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service
- /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service Enabled
Detected “cgroupfs” as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is “systemd”. The files located in /usr/lib/systemd/system or /lib/systemd/system contain the default options and should not be edited. Runtime directory and storage driver. You may want to control the disk space used for Docker images, containers and volumes by moving it to a separate partition. Systemctl start docker. Docker space issue for Mac. In case you are working on Mac and then you could try one more approach to free up some space by deleting Docker.raw file. Mac OS is a little special and it creates a docker.raw file for local docker storage and over time this file piles up. You can locate the file here. Jul 25 19:51:55 ubuntu systemd1: Stopped Docker Application Container Engine. Jul 25 19:51:55 ubuntu systemd1: docker.service: Start request repeated too quickly. Jul 25 19:51:55 ubuntu systemd1: docker.service: Failed with result 'exit-code'. Jul 25 19:51:55 ubuntu systemd1: Failed to start Docker Application Container Engine.
Ubuntu 16.04 LTS is now available. After having made the switch from 14.04 without really looking at the changes except for the kernel number (4.x), I was pleasantly surprised by the fact that it now uses systemd.Trying to setup docker to pull/push from a private registry using security, I first attempted to change the logging level to debug by adding -D in /etc/default/docker and after restarting docker noticed that no 'debug' logs were shown.
This took me a while to find out but /etc/default/docker is not used anymore.
This fact is in the /etc/default/docker file but easy to miss:
# Docker Upstart and SysVinit configuration file
 #
## THIS FILE DOES NOT APPLY TO SYSTEMD
#
# Please see the documentation for 'systemd drop-ins':
# https://docs.docker.com/engine/articles/systemd/
#
# Customize location of Docker binary (especially for development testing).
#DOCKER='/usr/local/bin/docker'
# Use DOCKER_OPTS to modify the daemon startup options.
DOCKER_OPTS='--dns 8.8.8.8 --dns 8.8.4.4'
# If you need Docker to use an HTTP proxy, it can also be specified here.
#export http_proxy='http://127.0.0.1:3128/'
# This is also a handy place to tweak where Docker's temporary files go.
#export TMPDIR='/mnt/bigdrive/docker-tmp'
Also, one can find out where a service file and configuration is located:
 $ systemctl show --property=FragmentPath docker
$ systemctl show --property=FragmentPath dockerFragmentPath=/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service
$ grep EnvironmentFile /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service
grep: /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service: No such file or directory
What the above tells us is that the docker service has no configuration file at the moment.
There are different ways to configure services in systemd. The option described below is OK but deviates from a standard systemd setup in the config location as, since this is Ubuntu, /etc/default path is used instead of /etc/sysconfig.
The first step to use a config file is to add the required informarion to the /lib/systemd/system/docker.service file by adding an EnvironmentFile attribute in the [Service] section:
$ vi /lib/systemd/system/docker.service
[Unit]
Description=Docker Application Container Engine
Documentation=https://docs.docker.com
After=network.target docker.socket
Requires=docker.socket
[Service]
Type=notify
# see https://docs.docker.com/engine/admin/systemd
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/default/docker
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker daemon -H fd:// $DOCKER_OPTIONS
$DOCKER_STORAGE_OPTIONS
$DOCKER_NETWORK_OPTIONS
$BLOCK_REGISTRY
$INSECURE_REGISTRY
MountFlags=slave
LimitNOFILE=1048576
LimitNPROC=1048576
LimitCORE=infinity
TimeoutStartSec=0
# set delegate yes so that systemd does not reset the cgroups of docker containers
/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service Permission Denied
Delegate=yes[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Now when the docker service is restarted it will use /etc/default/docker as its environment file, and pull the environment variables from it.
As such, the final step is to add the matching options in /etc/default/docker:

# Docker Upstart and SysVinit configuration file
# Customize location of Docker binary (especially for development testing).
#DOCKER='/usr/local/bin/docker'
# Use DOCKER_OPTS to modify the daemon startup options.
DOCKER_OPTS='--dns 8.8.8.8 --dns 8.8.4.4'
# If you need Docker to use an HTTP proxy, it can also be specified here.
#export http_proxy='http://127.0.0.1:3128/'
# This is also a handy place to tweak where Docker's temporary files go.
#export TMPDIR='/mnt/bigdrive/docker-tmp'
Docker /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service
INSECURE_REGISTRY='
/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service Enabled
DOCKER_STORAGE_OPTIONS='DOCKER_NETWORK_OPTIONS='
BLOCK_REGISTRY='
It should work.